What is the Mempool?
The mempool – short for memory pool – is the waiting area for unconfirmed Bitcoin transactions. When you create and sign a transaction, it doesn’t go straight into the blockchain. Instead, it first enters the mempool of a node, where it “waits” until a miner picks it up and includes it in a block.
Why does the Mempool exist?
Bitcoin transactions are confirmed in batches, usually about every 10 minutes, when a new block is mined. They don’t get confirmed one by one in real time.
The mempool stores new transactions temporarily, until a miner finds the next block. After each block is found, miners look into their mempool and select the transactions with the highest fees to include in the next block.
At the same time, the mempool acts as a filter. Before a transaction even enters the mempool, nodes check whether it’s valid. Invalid or conflicting transactions – for example, double spends – are rejected immediately and never enter the mempool.
The mempool also enables a kind of fee marketplace. Because the mempool shows all pending transactions along with their attached fees, users can estimate what fee rate (in sats/vByte) is appropriate before signing and sending a transaction. That helps you guess how long it will take to get confirmed.
Every Bitcoin node keeps its own local version of the mempool – there is no single global mempool. The mempools of different nodes are often very similar, but they don’t have to be 100% identical. Each node can decide its own rules, like how large its mempool can be or what the minimum fee must be for a transaction to be accepted.
How does a Transaction enter the Mempool?
When you click “Send” in your wallet, the software creates a valid, signed Bitcoin transaction. This transaction is then broadcast to the Bitcoin network. The first node that receives it will check the transaction: Is the input really spendable? Is the signature valid? Does it follow the consensus rules? If yes, the transaction is added to that node’s local mempool.
From there, the transaction spreads through the network. Each node that accepts it forwards it to its peers. Within seconds, the transaction reaches many nodes and mempools around the world.
Miners constantly watch their own mempools for new transactions. They usually prioritize the ones with higher fees, because those are more profitable. Once a miner has selected a set of transactions, it tries to find a valid hash to create a new block. If it succeeds, the block is sent to the network. Other nodes verify the block, and if it’s valid, they add it to the blockchain. All transactions inside that block are now considered confirmed.
With each additional block that is mined afterward, the number of confirmations increases. As a rule of thumb, six confirmations (usually around one hour) are considered final. But in most cases, even one confirmation is enough to consider the transaction secure and irreversible
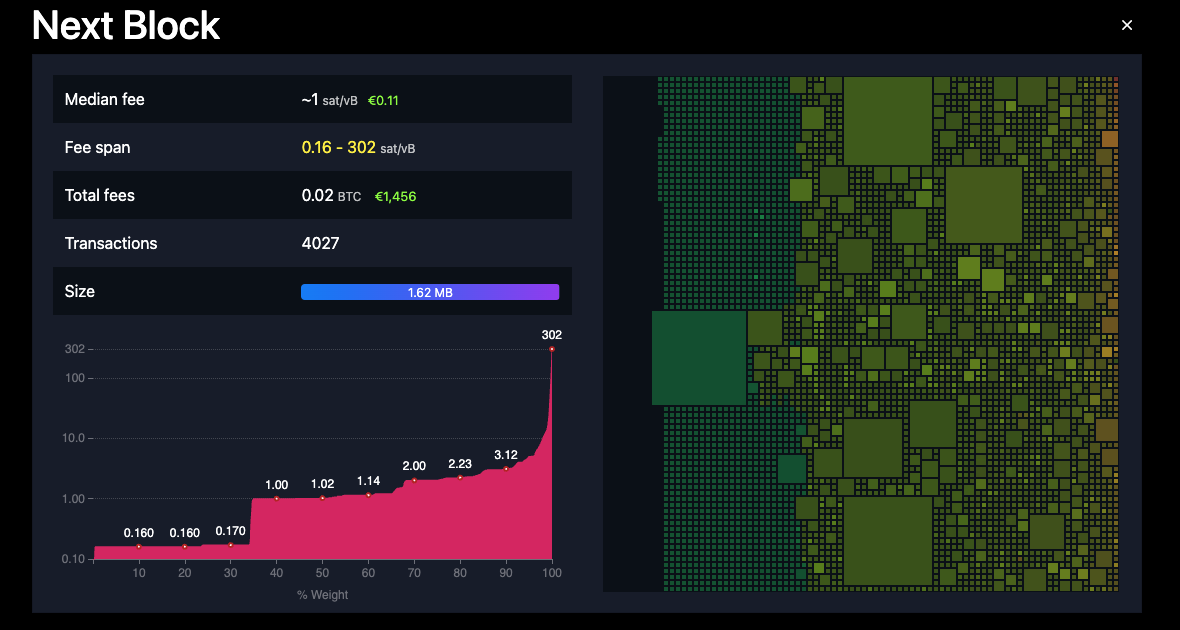
A visual representation of the mempool from mempool.space
Sometimes, confirmation takes longer than expected. This usually happens when many users are sending transactions at the same time – the demand for block space is high. In that case, miners will choose the most profitable transactions first – the ones with the highest fees.
Bitcoin nodes also have limits on how much space they allow for the mempool. If a node’s mempool is full, it starts dropping the transactions with the lowest fees. And if a transaction offers a fee that’s far too low, some nodes may reject it completely – meaning it won’t even enter the mempool. When that happens, the original coins (UTXOs) stay spendable in your wallet, as if the transaction never existed.
That’s why it’s helpful to check the current fee levels before sending a transaction – and set your fee according to how urgent the transfer is.
Final Thoughts
- The mempool is Bitcoin’s temporary waiting room for new transactions, before they are confirmed in a block.
- Every node maintains its own mempool – there is no central version.
- Transactions compete for block space. When the network is busy, transactions with low fees may have to wait longer.

